Paradigm Shifts
A paradigm shift is a fundamental change in the way that people think about or approach a particular problem or concept. In the context of making investment decisions, a paradigm shift could be an important factor to consider because it can affect the long-term viability of an investment,
Understanding paradigm shifts is crucial for investors, as these shifts can dramatically alter market landscapes, create new investment opportunities, or render existing strategies obsolete
The last 100 years
- 1920s = “Roaring”: From Boom to Bursting Bubble
- a time of great change and cultural upheaval. The decade began with the end of World War I, which had a profound impact on society and politics around the world. In the United States, the 1920s saw the rise of the "Roaring Twenties", a period of economic growth and prosperity, as well as the emergence of new cultural movements such as jazz music and the "Lost Generation" of writers and artists.
- Second Industrial Revolution / Technological Revolution (1870 - 1914). Technologies brought way more time and productivity to people's lives.
- Wall Street Crash of 1929 happened for overproduction, overspeculation, and a lack of regulation in the stock market. People borrowed money to buy stocks.
- 1930s = Depression
- The 1930s were a time of great economic and political turmoil around the world. The decade began with the Great Depression, a period of economic downturn that affected nearly every country and led to widespread unemployment and poverty. In the United States, the Depression (Roosevelt Recession) was addressed through the New Deal, a series of government programs and reforms aimed at boosting the economy and providing relief to those in need.
- In Europe, the Depression was a major factor in the rise of authoritarian regimes, includin Germany and Italy under Fascist regime. These countries pursued aggressive expansionist policies, leading to the outbreak of World War II in 1939. The war would go on to become one of the deadliest conflicts in human history, ultimately resulting in the defeat of the Axis powers and the creation of a new global order.
- 1940s = War and Post-War
- World War II (1939 - 1945) - the war led to advances in technology, medicine, and civil rights.
- In the US, as government spending dried up, the economy dipped into a serious recession with GDP contracting by a whopping 11 percent.
- Third Industrial Revolution / Digital Revolution (from 1947 the birth of first transistor)
- Cold War (1947 - 1991)
- 1950s = Post-War Recovery
- In the U.S., the 1950s are often remembered as a time of economic prosperity and cultural conformity, as the country experienced a period of rapid growth and the rise of suburban communities.
- monolithic integrated circuit (1959)
- 1960s = From Boom to Monetary Bust
- The 1960s saw significant developments in science and technology, with the first manned space missions and the emergence of the personal computer. In popular culture, the 1960s were marked by the rise of the counterculture and the hippie movement, as well as the emergence of new musical genres such as rock and roll and psychedelia.
- ARPANET / Internet (1969)
- The U.S. was running large budget and trade deficits, and other countries were starting to lose confidence in the dollar's ability to maintain its value, which resulted in ending the Bretton Woods monetary system (1973).
- 1970s = Low Growth and High Inflation (i.e., Stagflation).
- The decade began with the end of the Vietnam War and the Watergate scandal, which shook the United States and led to a period of political and social upheaval. In Europe, the 1970s saw the rise of terrorism and the emergence of new political movements, such as feminism and environmentalism. Home appliance boom moved more women into the workforce, and then economic independence.
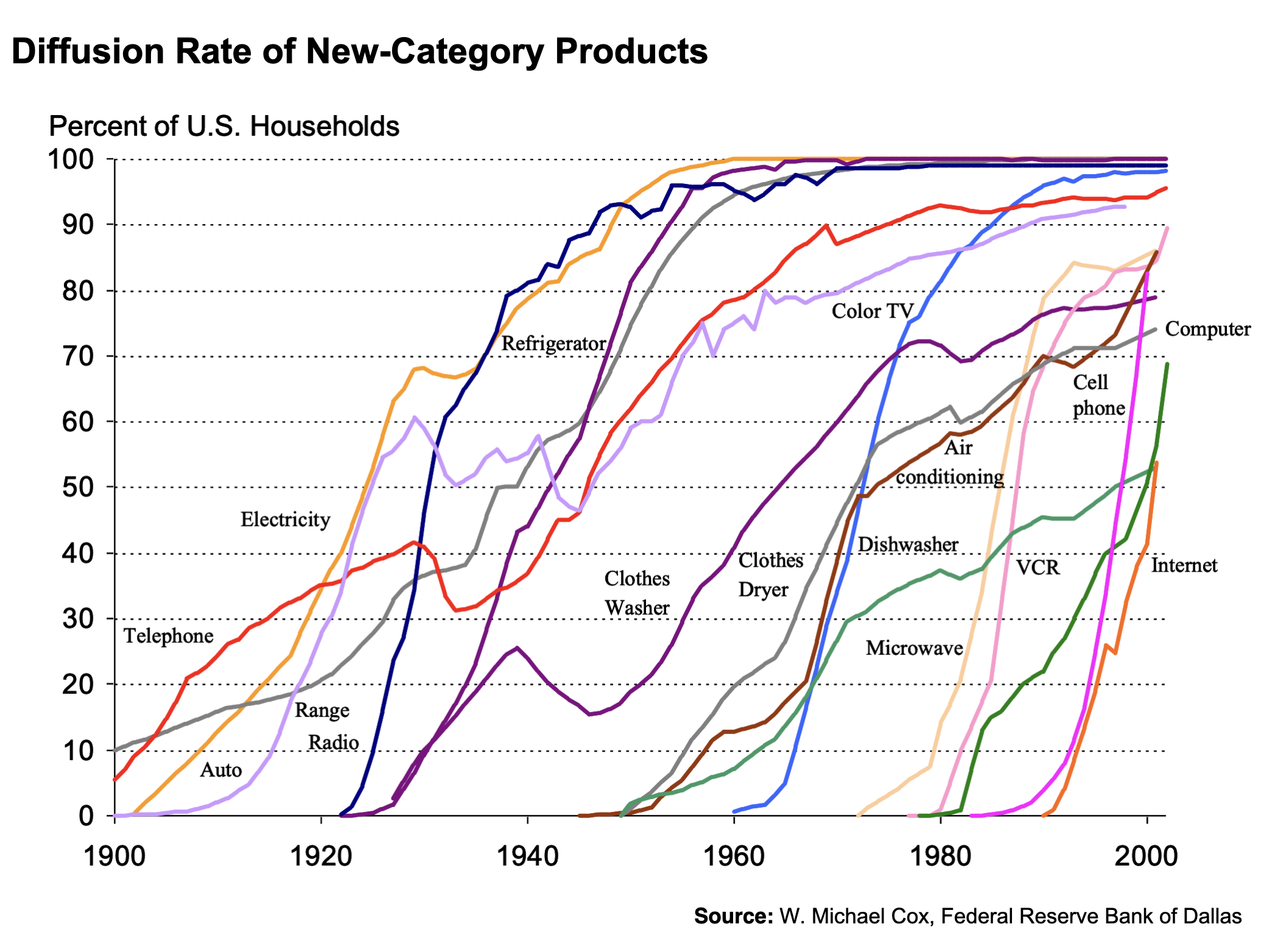
- The 1970s were also a time of economic turmoil, as the global economy was affected by rising oil prices, inflation, and stagnant growth. In the United States, the 1970s saw the end of the post-World War II economic boom and the beginning of a period of slow growth and high unemployment.
- 1980s = High Growth and Falling Inflation (i.e., Disinflation).
- a time of economic growth and globalization, as advances in technology and communication led to increased trade and investment around the world. In the United States, the 1980s saw the rise of the "yuppie" culture, as well as the emergence of new industries, such as personal computing and biotechnology.
- 1990s = “Roaring”: From Bust to Bursting Bubble.
- The decade began with the collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, which had a profound impact on global politics and economics. In the United States, the 1990s saw the rise of the internet and the emergence of new technologies, such as the World Wide Web and personal computers.
- The 1990s were also a time of economic growth and globalization, as advances in technology and communication led to increased trade and investment around the world. In the United States, the 1990s saw the rise of the "dot-com" boom, as well as the emergence of new industries, such as e-commerce and online advertising.
- 2000-10 = “Roaring”: From Boom to Bursting Bubble.
- The decade began with the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, which had a profound impact on global politics and security. In the United States, the 2000s saw the election of President George W. Bush and the beginning of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.
- The 2000s were also a time of economic growth and globalization, as advances in technology and communication continued to drive trade and investment around the world. In the United States, the 2000s saw the emergence of new industries, such as social media and mobile technology, as well as the Great Recession of 2008, which had a profound impact on the global economy.
- 2010-2020 = Reflation
- Reflation is an economic policy designed to stimulate an economy by increasing the money supply and driving down interest rates. This can be accomplished through a variety of methods, such as lowering taxes, increasing government spending, or implementing quantitative easing measures. The goal of reflation is to boost economic growth and reduce unemployment by making it easier for individuals and businesses to borrow money and invest in new projects. In addition, reflation is often used as a response to deflation, which is a sustained period of falling prices and economic stagnation.
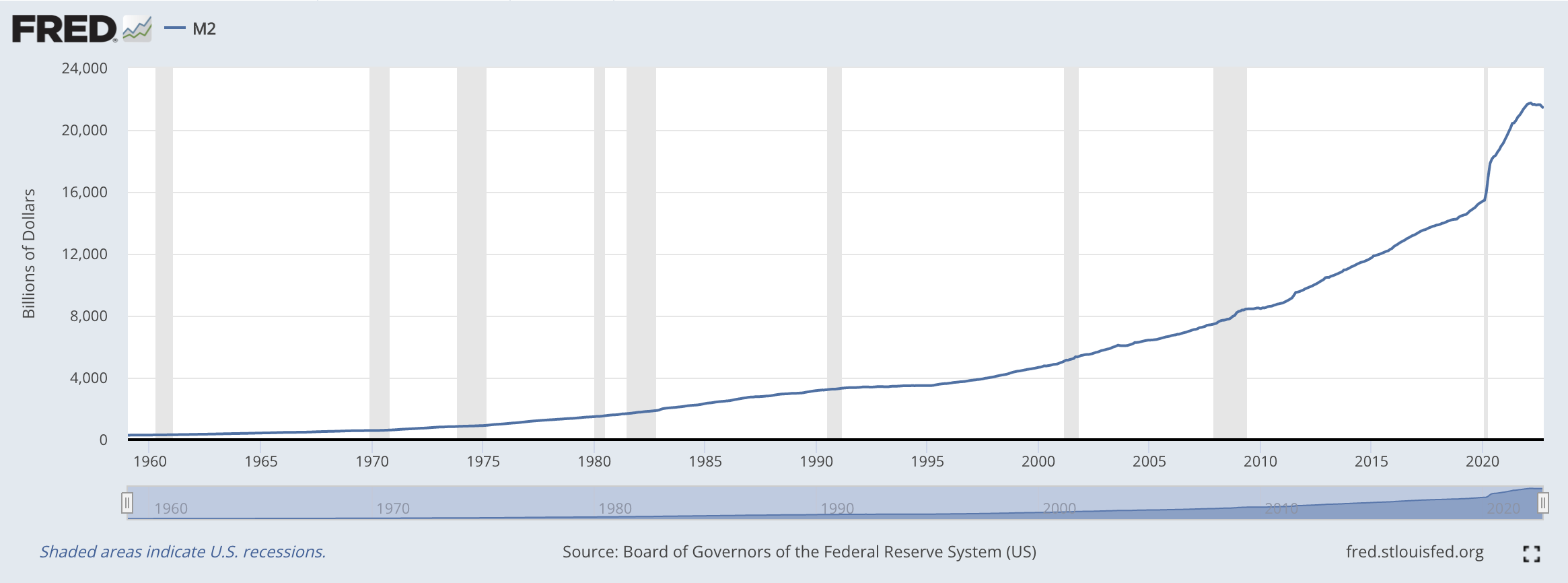
- Mobile was eating the world
- The US can no longer assume that every hot new thing will be made in the US
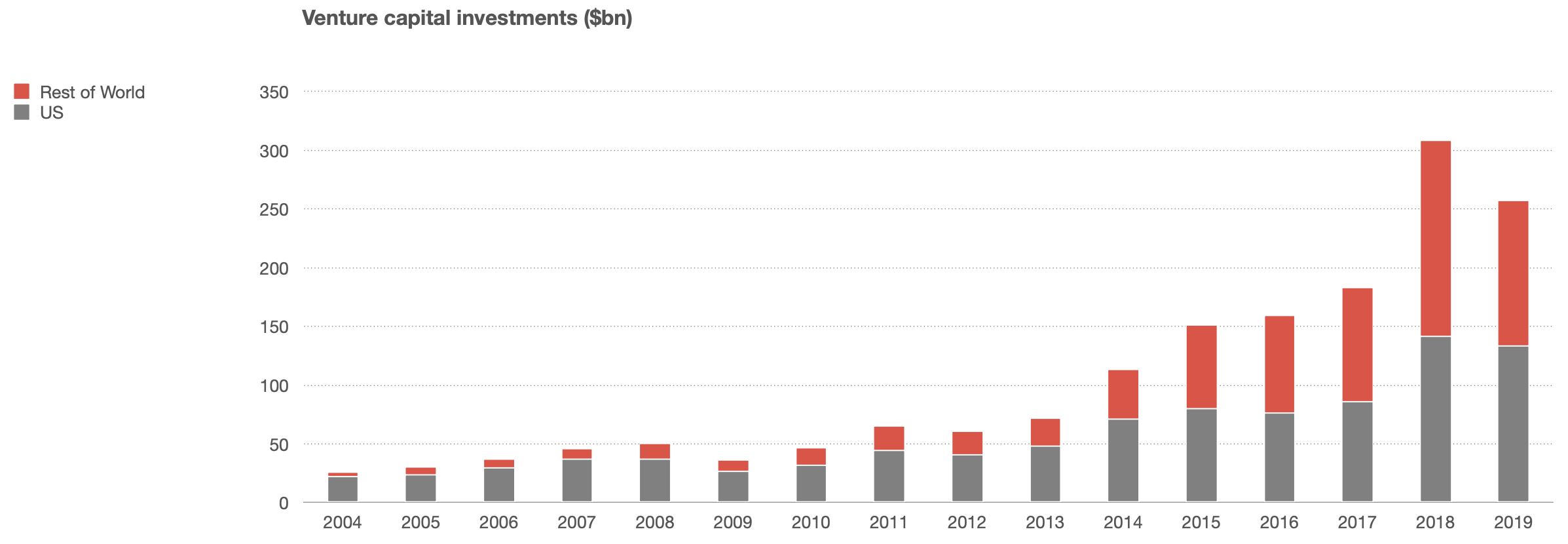
- 2020-Now = ?
- Reflation reached the top after COVID-19, and quantitative easing led to increased economic growth and higher inflation.
- At the end of 2022, The economy is facing several challenges, including high inflation, rising interest rates, fears of a recession, the lingering effects of the recent pandemic, disruptions to supply chains, rising gas prices, and, particularly in Europe, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. These factors are contributing to economic strains and uncertainty.
Sources: Principles: Paradigm Shifts, U.S. Economic Recessions: Causes, Impacts & History, Benedict Evans